Creating a green roof with sod is an excellent way to bring nature into urban spaces, improve air quality, and reduce energy costs. Green roofs offer a range of environmental benefits, including insulation, stormwater management, and the reduction of urban heat islands. This article will guide you through the process of creating a green roof with sod, from planning and preparation to installation and maintenance.
Planning Your Green Roof
Before starting your green roof project, careful planning is essential. The first step is to assess the structural integrity of your building. Not all roofs are designed to support the additional weight of a green roof, so it’s important to consult with a structural engineer. The weight of the sod, soil, and water needs to be factored in to ensure the roof can handle the load.
Next, consider the purpose of your green roof. Are you looking to create a space for leisure, improve insulation, or enhance biodiversity? Your goals will influence the design and choice of materials. For example, a roof intended for recreational use may require different structural supports and access points compared to one aimed primarily at environmental benefits.
Finally, check local regulations and building codes. Some municipalities have specific requirements for green roofs, including permits, safety standards, and design guidelines. Ensuring compliance with these regulations will help avoid legal issues and ensure your project meets all necessary standards.
Selecting the Right Sod
Choosing the appropriate type of sod for your green roof is crucial for its success. The sod needs to be hardy, drought-tolerant, and capable of thriving in the specific conditions of a rooftop environment. Factors such as sunlight exposure, wind, and temperature variations should be considered when selecting sod.
Cool-season grasses, such as fescues and ryegrass, are ideal for regions with colder climates. These grasses are hardy and can withstand low temperatures, making them suitable for green roofs in northern regions. Warm-season grasses, like Bermuda and zoysia, are better suited for warmer climates, as they are more drought-tolerant and thrive in higher temperatures.
Additionally, consider using a mix of grass species to enhance biodiversity and resilience. A diverse mix can improve the overall health of the green roof by reducing susceptibility to pests and diseases. Consulting with a local nursery or green roof specialist can provide valuable insights into the best sod varieties for your specific location and conditions.
Preparing the Roof
Proper preparation of the roof is essential for the longevity and effectiveness of your green roof. Start by installing a waterproof membrane to protect the underlying roof structure from water damage. This membrane acts as a barrier, preventing water from seeping through and causing leaks.
Next, add a root barrier to prevent plant roots from penetrating the waterproof membrane and damaging the roof structure. The root barrier is typically a layer of durable plastic or rubber that blocks roots while allowing water to drain through. This layer is crucial for maintaining the integrity of the roof over time.
Install a drainage layer on top of the root barrier to ensure proper water management. This layer typically consists of lightweight gravel or specialized drainage mats that allow excess water to flow away from the sod. Proper drainage is essential to prevent waterlogging, which can damage the grass and the roof structure.
Adding the Growing Medium
The growing medium, or soil layer, is a critical component of a green roof. It provides the necessary nutrients for the sod and supports plant growth. The soil used for green roofs is typically a lightweight mix of organic and inorganic materials, designed to retain moisture while providing adequate drainage.
When choosing a growing medium, consider its weight, water retention capacity, and nutrient content. A typical green roof soil mix includes components like expanded clay, perlite, compost, and sand. These materials help create a lightweight, well-draining soil that can support plant growth without adding excessive weight to the roof.
Spread the growing medium evenly across the roof to a depth of 4 to 6 inches, depending on the type of plants and the structural capacity of the roof. Ensure the soil is level and free of debris before proceeding with the sod installation. Properly preparing the growing medium will promote healthy root development and ensure the success of your green roof.
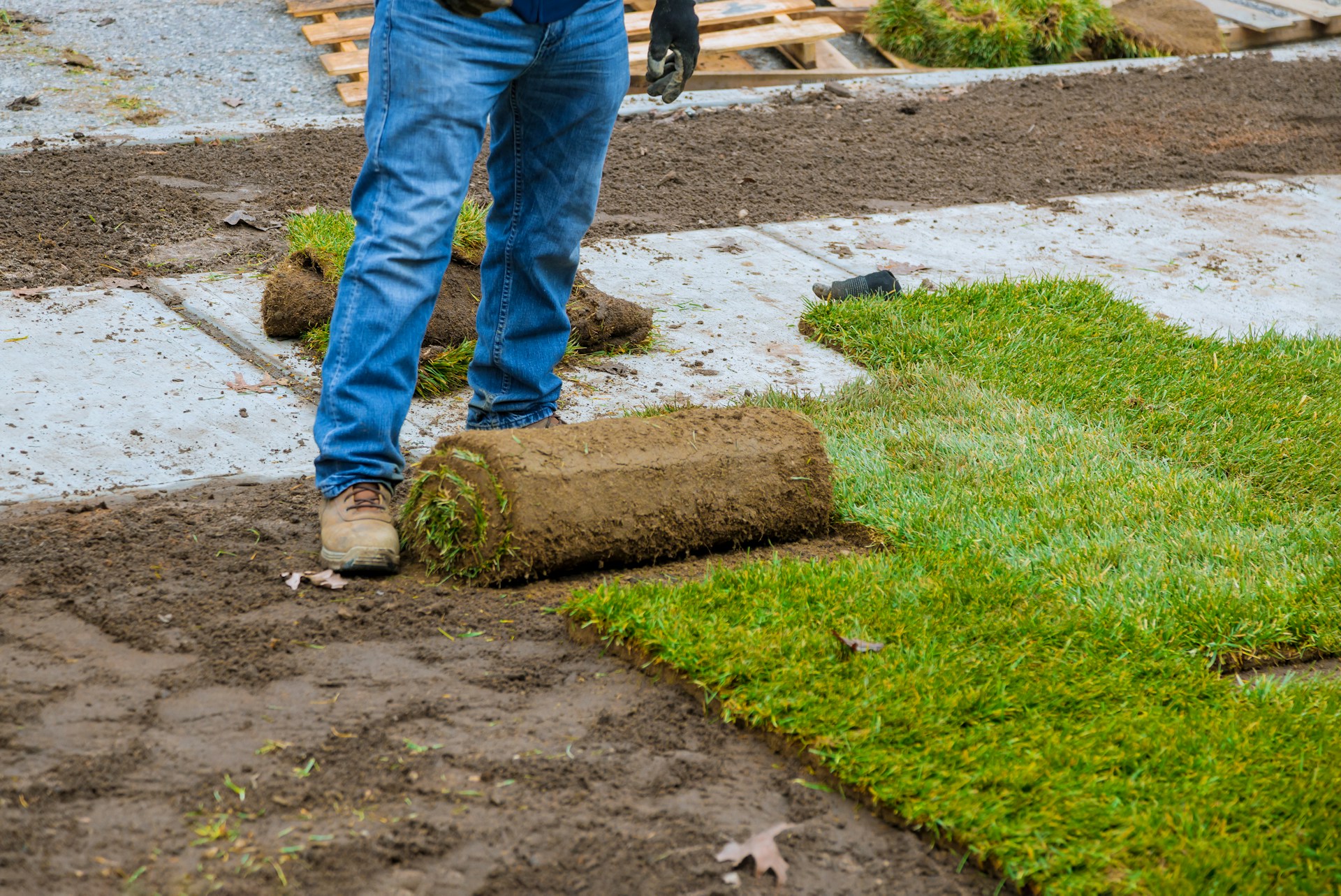
Installing the Sod
With the roof prepared and the growing medium in place, it’s time to install the sod. Start by measuring and cutting the sod to fit the roof dimensions. It’s important to lay the sod in a staggered pattern, similar to laying bricks, to prevent seams from aligning and creating weak spots.
Begin laying the sod from one corner of the roof, working your way across in a systematic manner. Press the edges of each sod piece firmly together to avoid gaps. This ensures that the sod establishes quickly and uniformly. Water the sod immediately after installation to help it settle and start the rooting process.
After laying all the sod, use a roller to press it firmly into the growing medium. This step is crucial for eliminating air pockets and ensuring good contact between the sod roots and the soil. Proper contact promotes root growth and helps the sod establish more quickly.
Watering and Maintenance
Watering is critical in the initial stages of establishing a green roof with sod. For the first few weeks, water the sod daily to keep the soil consistently moist. This encourages deep root growth and helps the sod establish itself. Gradually reduce the frequency of watering as the sod becomes established.
Regular maintenance is essential to keep the green roof healthy and vibrant. This includes mowing the grass to the appropriate height, removing weeds, and applying fertilizer as needed. Monitoring the health of the sod and addressing any issues promptly will ensure the long-term success of your green roof.
In addition to routine maintenance, seasonal care is important. In the spring and fall, apply a balanced fertilizer to provide essential nutrients for growth. During the winter, ensure proper drainage to prevent water from freezing and damaging the roof. Regular inspections and maintenance will keep your green roof in top condition throughout the year.
Addressing Common Challenges
Creating and maintaining a green roof with sod can come with its challenges. One common issue is water management. Proper drainage is crucial to prevent waterlogging and root rot. Ensure your drainage system is functioning correctly and adjust your watering schedule based on weather conditions and the needs of the sod.
Pest control is another important aspect of green roof maintenance. Monitor the sod for signs of pests such as insects and rodents. Implement integrated pest management strategies, including natural predators, to control pest populations without harming the environment. Regular inspections can help detect and address pest issues before they become severe.
Weed management is also essential to maintaining a healthy green roof. Weeds can compete with sod for nutrients and water, reducing its vitality. Regularly inspect your green roof for weeds and remove them promptly. Mulching can help suppress weed growth and maintain soil moisture.
Benefits of a Green Roof with Sod
Green roofs offer numerous benefits, both environmental and economic. One of the primary advantages is improved insulation. The additional layers of sod, soil, and vegetation provide thermal insulation, reducing the energy needed to heat and cool the building. This results in lower energy bills and a reduced carbon footprint.
Green roofs also contribute to stormwater management. The vegetation and soil absorb rainwater, reducing runoff and alleviating pressure on stormwater systems. This helps prevent flooding and improves water quality by filtering pollutants. In urban areas, green roofs play a crucial role in managing stormwater and mitigating the effects of heavy rainfall.
Additionally, green roofs enhance urban biodiversity. They provide habitats for various plant and animal species, promoting ecological diversity in city environments. Green roofs can attract pollinators such as bees and butterflies, contributing to the health of urban ecosystems. By creating green spaces in urban areas, green roofs help reconnect city dwellers with nature.
Conclusion
Creating a green roof with sod is a rewarding project that offers numerous environmental, economic, and aesthetic benefits. Proper planning, selection of the right materials, and regular maintenance are key to ensuring the success of your green roof. By transforming an ordinary roof into a vibrant green space, you can contribute to a healthier and more sustainable urban environment.